PRODUCT- MoS2 Lubricating Coating Agent -
MoS2 Lubricating Coating Agent
LUBRICATING COATING
When a metal comes into contact with another metal and rubs against each other, friction occurs. This friction generates heat, vibration and noise, and also wears down the metal surfaces, and in the worst case can destroy the weaker metal. To prevent this, it is necessary to reduce friction by using a lubricant between metals. Generally, oil or grease is used as a lubricant. (In some cases, one of the metals is replaced with plastic to avoid the worst case of the metal seizure.) When metal-to-metal contact involves high-speed sliding or load-bearing, regular oil or grease is often insufficient as a lubricant. Oil or grease containing friction reducers or extreme pressure agents are required.
However, over time the oil will evaporate little by little and its quality will deteriorate, and then it will no longer function properly as a lubricant. Also, if dirt or dust adheres to the oil or grease due to surrounding conditions, it can actually hinder lubrication.
For this reason, lubricating coating is used as a dry lubricant that retains their lubricating properties for long periods of time and are resistant to the adhesion of dirt and other particles.
This lubricating coating agent is made by dispersing solid lubricants in a binder resin to smooth the surface and increase lubricity of the sliding surface and is fixed to the metal surface by baking. Although the surface of the coating agent wears away due to sliding, etc., the solid lubricant remains and maintains its lubricating function.
In addition, since the surface becomes dry after baking, it is less likely to become contaminated by dirt or other particles. Additionally, there is also a simple method of providing lubricity to metal surfaces using an aerosol product that contains dispersed solid lubricants.
Examples of LUBRICATING COATING
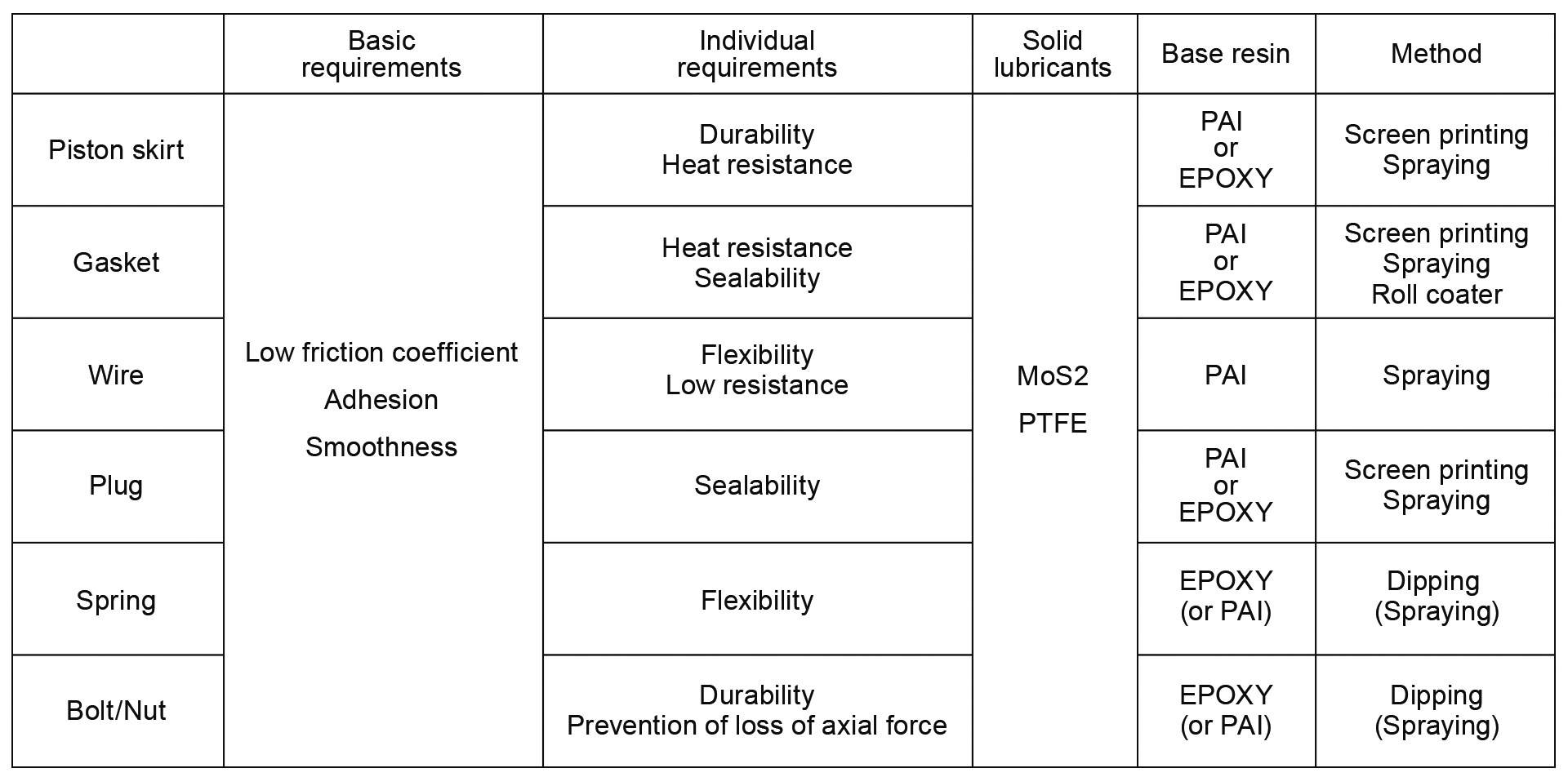
The main purpose of using Mos2 coating on metal surfaces is to reduce friction caused by metal-to-metal contact, but to achieve this goal over a long period of time, adhesion to the metal and surface smoothness are also required. In addition, different properties are required for each part.
A.Engine piston skirt

The engine piston moves in an elliptical motion at high speed inside the cylinder. Therefore, friction occurs repeatedly between the cylinder and the piston skirt. Engine oil cannot reduce this sufficiently. Therefore, applying a lubricating coating to this part reduces friction, reduces heat, vibration, and noise generation, and achieves a longer life for the parts. The coating used for this is required to be durable and heat resistant.
B.Engine head gasket

The engine head gasket uses a sealant to prevent leakage of coolant and oil, but this sealant is affected by vibration and heat generated by the engine, and in the worst case, cracks will occur. In addition, the head gasket is subjected to friction from both the body and head of the engine. To reduce this, a lubricating coating is applied to the head gasket. The coating used for this is required to be heat resistant and airtight.
C.Endoscope wire

Some endoscopes have a mechanism that allows the camera at the tip to be operated by hand. This operation is performed by operating multiple wires that pass through a thin tube connecting the tip and the hand. These multiple wires come into contact with each other and rub against the guide rings, causing friction. To reduce this and improve operability, it is necessary to apply a lubricating coating to the surface of the wires. Since endoscopes move flexibly, the coating used on the internal wires must be flexible and have low resistance.
D.Gas valve

When opening and closing a gas valve, friction occurs between the internal parts. To reduce this friction and to prevent gas leakage due to the wear between parts, a lubricating coating on the surface of the part and long-lasting grease are necessary. This coating with the grease must be airtight and sealable.
E.Spiral spring

A spiral spring is used in the mechanism that reclines and returns the seat in a car to its original position. When the seat is reclined, force is applied to the spring, causing it to deform, and the force that returns it to its original position accumulates. By applying a lubricating coating to the surface of the spiral spring, creaking noise, vibration, and heat generation are suppressed, and the parts have a longer life. The coating used on the spring must be flexible.
F.Bolts and Nuts

In order to efficiently transmit the force (torque) when tightening a bolt, it is necessary to reduce friction and prevent a decrease in axial force. Also, when tightening with a strong torque, the bolt and nut may become seized. Friction can be reduced by applying a lubricating coating to the bolts and nuts. Coatings used on bolts and nuts must be durable.
MoS2 COATING AGENT
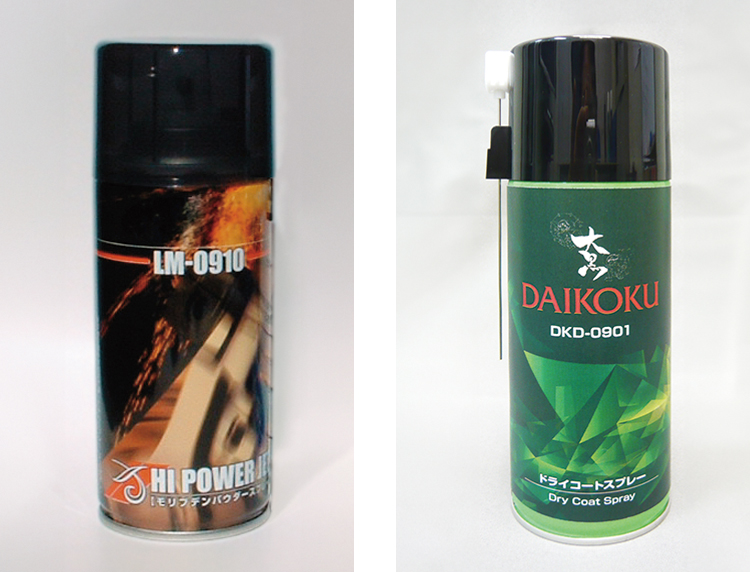
A lubricating coating is generally made from solid lubricants and a resin. Solid lubricants include graphite, molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), PTFE, etc., while resins include PAI (Polyamide-imide) and EPOXY, etc.
Daito’s lubricating coating agents use Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) and PTFE as the solid lubricants, and either PAI (Polyamide-imide) or EPOXY as the resin. MoS2 is an excellent solid lubricant with a low friction coefficient, and good adhesion to a metal surface. And we should consider which size of MoS2 to use as there are some different particle sizes. The combination of MoS2 and PTFE as the solid lubricants perform a high synergy effect and reduces the friction coefficient. We should consider which resin to use as a base resin to satisfy the requirements because each resin has its own characteristics. Daito has developed the optimal coating agents through mechanical and chemical dispersion.
Comparison table between our products and another company's product
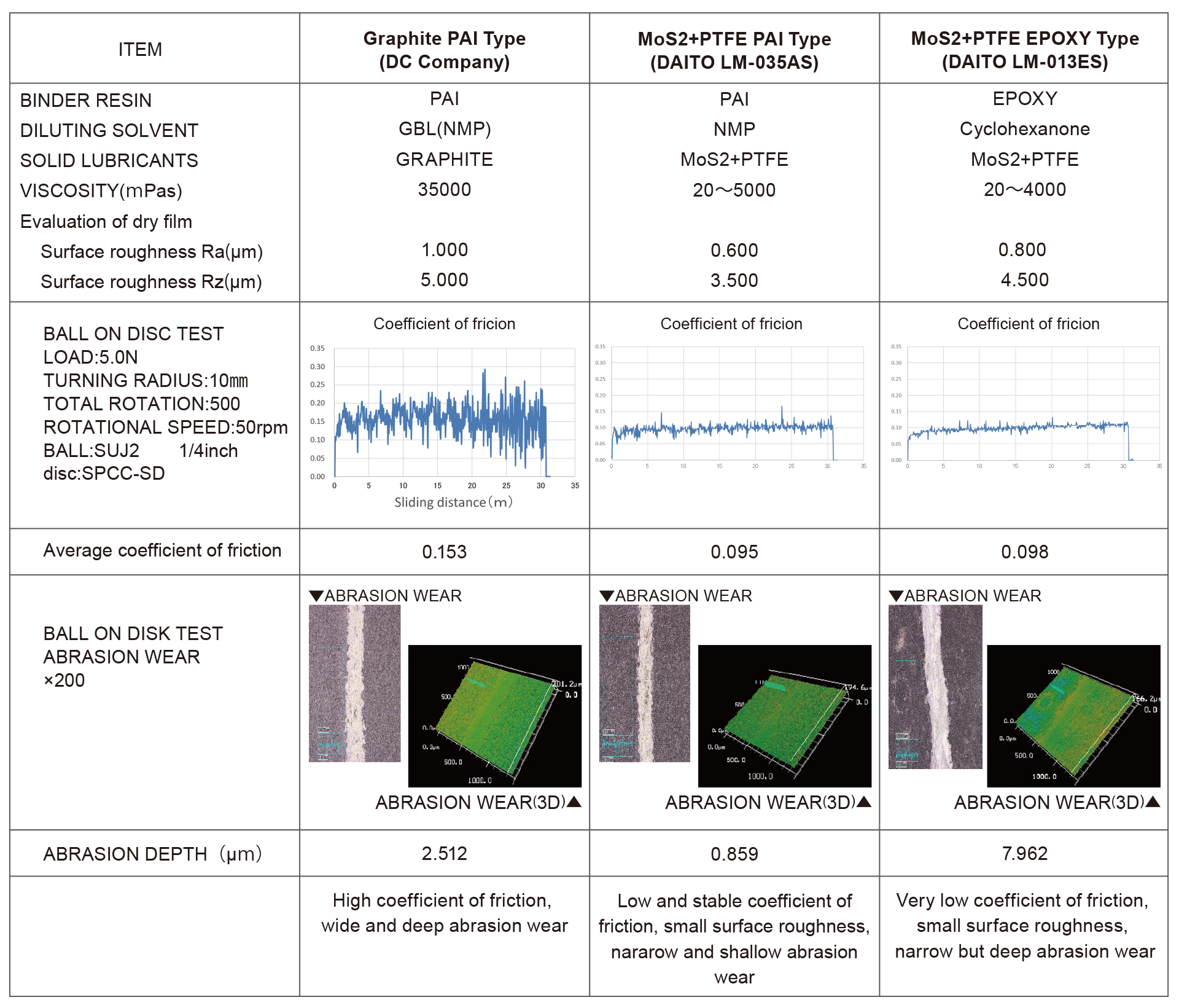
DAITO develops designs to meet these individual requirements. Film thickness, film strength, baking temperature, time, etc. are finalized through prototyping, testing, and evaluation at the individual design stage.
COATING PROCESS
-
Before coating, remove oil and dirt from the surface of the parts.
Wash the parts with warm water and dry them quickly to prevent rust. If oil remains on the parts when coating, adhesion to the metal may be impaired and the coating film may peel off. -
Coat the metal surface (see below for coating method).
Coating agents using PAI resin are prone to moisture absorption, so care must be taken with the coating method and working environment. Pre-drying is also performed to prevent moisture absorption after application. -
The coating film is fixed to the metal surface by baking. The baking temperature and time vary depending on the coating liquid and the size of the parts. The baking time is the time after the parts reach the baking temperature.
-
After baking, check that the temperature has dropped and store the parts. At this time, care must be taken not to damage the coating film due to contact between parts.
COATING METHOD
There are several methods for coating, including screen printing, spraying, and dipping. The most suitable method is selected from among them depending on the size and shape of the part, the required film thickness, etc.
-
Screen printing is a method of coating the necessary parts using a screen printing machine and a screen, and is suitable for coating flat surfaces, and the sides of cylinders or cones. The film thickness is controlled by selecting the screen and adjusting the concentration of the coating agent.
-
Spraying is a method of spraying the agent using a spray gun, and does not matter the shape of the part, but it requires not only a spray device but also the installation of a spray booth. Since PAI resin absorbs moisture, the temperature and humidity in the booth must be controlled to a certain constant level. In addition, since a diluting solvent is used in the coating agent, it may be necessary to take measures for the applicator.
-
Dipping is a method of immersing the part in the coating agent, and is suitable for coating the entire part, but is not suitable for controlling the film thickness precisely. After coating, the excess coating agent is removed by spinning or other methods.
COATING, STORAGE, and etc.
When diluting MoS2 coating agent with a solvent and applying it to parts, it is necessary to take measures to prevent workers from being exposed to the solvent (glasses, masks, gloves, work clothes, etc.) and exhaust equipment (local exhaust, general ventilation, etc.). (Please check the contents of the product's SDS and follow national laws and regulations.)
MoS2 lubricant coating agent may be affected by temperature and humidity. In particular, for PAI resin, work should be done at a temperature of 10℃ to 30℃ and a humidity of less than 60%.
There are certain temperature conditions for storing MoS2 lubricant coating agent. It is not classified as a hazardous material, but dilution solvents are generally classified as hazardous materials, so storage must comply with laws and regulations. (Please follow national laws and regulations.)
MoS2 Lubricating Coating
MoS2 SPRAY COATING PRODUCTS
Simple lubricating coating with a spray product
DKD-0910 is a spray product of MoS2 powder. By applying it directly to a metal surface, a simple coating film of MoS2 is formed.
In addition, DKD-0901 is applied directly to a metal surface to form a simple coating film of MoS2.

